Chapter 12 ap stats test – Prepare to conquer the Chapter 12 AP Statistics Test with confidence! This comprehensive guide provides a captivating overview of the test, empowering you with the knowledge and strategies to excel.
Delve into the intricacies of probability distributions, sampling and estimation, hypothesis testing, regression analysis, correlation and causation, and nonparametric tests. Master the art of statistical analysis and unlock the secrets to success on the AP Statistics Test.
Chapter 12 AP Statistics Test Overview
The Chapter 12 AP Statistics Test assesses students’ understanding of statistical inference for proportions.
The test covers topics such as:
- Estimating a population proportion
- Testing hypotheses about a population proportion
- Confidence intervals for a population proportion
To prepare for the test, students should:
- Review the material covered in class and the textbook.
- Practice solving problems similar to those that will appear on the test.
- Take practice tests to identify areas where they need additional study.
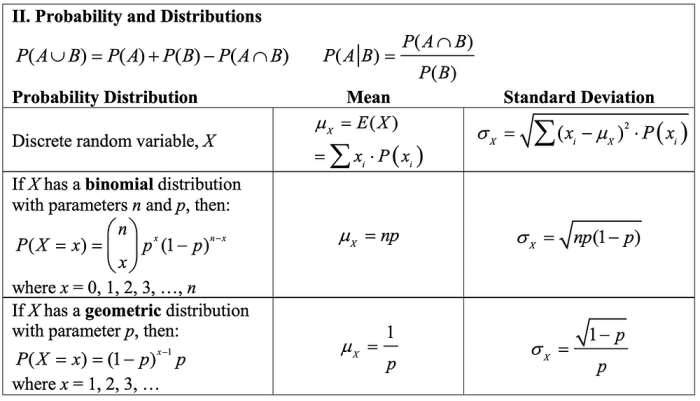
Probability Distributions
Probability distributions are mathematical functions that describe the likelihood of different outcomes occurring in a random experiment. They are used to model the behavior of random variables, which are variables that take on different values with varying probabilities.Probability distributions are essential for understanding the behavior of random processes and making predictions about future outcomes.
They are used in a wide variety of fields, including statistics, finance, engineering, and biology.
Types of Probability Distributions
There are many different types of probability distributions, each with its own unique properties. Some of the most common types of probability distributions include:
- Discrete distributions: Discrete distributions take on only a finite or countable number of values. Examples of discrete distributions include the binomial distribution, the Poisson distribution, and the hypergeometric distribution.
- Continuous distributions: Continuous distributions take on any value within a specified range. Examples of continuous distributions include the normal distribution, the t-distribution, and the chi-square distribution.
- Mixed distributions: Mixed distributions are a combination of discrete and continuous distributions. They are used to model situations where some outcomes are discrete and others are continuous.
Calculating Probabilities Using Probability Distributions
Once you have identified the type of probability distribution that best models your data, you can use that distribution to calculate the probability of any given outcome. The formula for calculating the probability of an outcome using a probability distribution is:“`P(X = x) = f(x)“`where:* P(X = x) is the probability of the outcome x
f(x) is the probability density function (PDF) of the distribution
The PDF is a function that describes the probability of each possible outcome. For discrete distributions, the PDF is a simple probability mass function (PMF). For continuous distributions, the PDF is a more complex function that takes into account the range of possible outcomes.
Examples of Probability Distributions in Real-World Situations
Probability distributions are used in a wide variety of real-world situations. Here are a few examples:
- The binomial distributionis used to model the number of successes in a sequence of independent trials, each of which has a constant probability of success.
- The Poisson distributionis used to model the number of events that occur in a fixed interval of time or space.
- The normal distributionis used to model a wide variety of continuous variables, such as the height of people or the weight of animals.
- The t-distributionis used to model the distribution of sample means when the population standard deviation is unknown.
- The chi-square distributionis used to test the goodness of fit of a model to data.
Sampling and Estimation
Sampling and estimation are two important statistical methods used to make inferences about a population based on a sample. Sampling involves selecting a representative subset of a population to study, while estimation uses the sample data to make predictions about the population parameters.
Types of Sampling Methods
There are different types of sampling methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
-
-*Simple random sampling
Each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected.
-*Systematic sampling
Members of the population are selected at regular intervals.
-*Stratified sampling
The population is divided into strata, and then a simple random sample is taken from each stratum.
-*Cluster sampling
The population is divided into clusters, and then a simple random sample of clusters is taken.
Calculating Confidence Intervals
A confidence interval is a range of values that is likely to contain the true population parameter. The width of the confidence interval depends on the sample size, the variability of the data, and the desired level of confidence.The formula for calculating a confidence interval for a population mean is:“`CI = x̄ ± z
(s/√n)
Chapter 12 of the AP Statistics test covers a wide range of topics, including hypothesis testing and confidence intervals. While studying for this chapter, you may find yourself thinking about the many applications of statistics in the real world. For example, a recent study published in the journal “The American Statistician” found that the USS Boorda Hall BEQ 30 has the highest average room temperature of all the BEQs on base.
This information could be useful for students who are looking for a warm place to live on base. USS Boorda Hall BEQ 30 . Returning to the AP Statistics test, it’s important to remember that practice is key. The more you practice, the better prepared you’ll be on test day.
“`where:
- CI is the confidence interval
- x̄ is the sample mean
- z is the z-score corresponding to the desired level of confidence
- s is the sample standard deviation
- n is the sample size
Examples of Sampling and Estimation in Research
Sampling and estimation are used in a wide variety of research studies. For example, a researcher might use a sample of students to estimate the average GPA of all students at a university. Or, a researcher might use a sample of voters to estimate the percentage of voters who will vote for a particular candidate in an election.
Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method used to determine whether a hypothesis about a population parameter is supported by the available evidence. It involves making a claim about the population parameter, collecting data from a sample, and using statistical methods to determine whether the data is consistent with the claim.
Steps Involved in Hypothesis Testing
- State the null and alternative hypotheses.
- Set the significance level.
- Collect a sample and calculate the test statistic.
- Determine the p-value.
- Make a decision about the null hypothesis.
Types of Hypothesis Tests
There are two main types of hypothesis tests:
- One-tailed tests: These tests are used when there is a specific direction to the alternative hypothesis.
- Two-tailed tests: These tests are used when there is no specific direction to the alternative hypothesis.
Examples of Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is used in a wide variety of research settings. Here are a few examples:
- A pharmaceutical company wants to test whether a new drug is effective in reducing cholesterol levels. The company would conduct a hypothesis test to determine whether the mean cholesterol level of patients taking the drug is lower than the mean cholesterol level of patients taking a placebo.
- A political scientist wants to test whether there is a relationship between political ideology and voting behavior. The scientist would conduct a hypothesis test to determine whether the proportion of people who vote for a particular party is different for people with different political ideologies.
Regression Analysis

Regression analysis is a statistical technique used to understand the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. It helps researchers determine how changes in the independent variables affect the dependent variable.Regression analysis is commonly used in various fields, including economics, finance, social sciences, and healthcare.
For instance, it can be used to predict stock prices based on economic indicators, analyze the impact of advertising campaigns on sales, or study the relationship between lifestyle factors and disease risk.
Types of Regression Models
There are several types of regression models, each with its own assumptions and applications:
-
-*Simple linear regression
Examines the relationship between a single independent variable and a single dependent variable.
-*Multiple linear regression
Considers the relationship between multiple independent variables and a single dependent variable.
-*Logistic regression
Used to model binary outcomes, such as whether an individual will experience a particular event or not.
-*Nonlinear regression
Captures relationships that are not linear in nature.
Examples of Regression Analysis in Research
-
-*Predicting housing prices
Using multiple linear regression to determine the relationship between housing prices and factors such as square footage, number of bedrooms, and location.
-*Evaluating the effectiveness of a new drug
Employing logistic regression to assess whether a new drug is effective in reducing disease symptoms.
-*Understanding consumer behavior
Using nonlinear regression to model the relationship between product price and consumer demand.
Correlation and Causation
Correlation and causation are two distinct concepts that are often confused. Correlation refers to the relationship between two variables, while causation refers to the relationship between a cause and its effect. Correlation does not imply causation, and it is important to be aware of the dangers of confusing the two.
Dangers of Confusing Correlation with Causation, Chapter 12 ap stats test
- Spurious correlations:These are correlations that appear to exist but are actually due to a third variable. For example, there is a strong correlation between ice cream sales and drowning deaths. However, this correlation does not mean that ice cream causes drowning.
It is more likely that both ice cream sales and drowning deaths are caused by a third variable, such as warm weather.
- Reverse causation:This occurs when the effect of a variable is actually the cause of the variable. For example, there is a strong correlation between smoking and lung cancer. However, this correlation does not mean that smoking causes lung cancer. It is more likely that lung cancer causes people to smoke.
Nonparametric Tests
Nonparametric tests, also known as distribution-free tests, are statistical tests that do not assume the underlying data follows a specific distribution, such as the normal distribution. They are used when the data is ordinal or categorical, or when the sample size is small and the assumption of normality cannot be made.
There are several different types of nonparametric tests, each designed to test different hypotheses about the data. Some of the most common nonparametric tests include:
Chi-square test
The chi-square test is used to test the independence of two categorical variables. It is often used to compare observed frequencies to expected frequencies, or to test whether a sample is representative of a population.
Mann-Whitney U test
The Mann-Whitney U test is used to compare the medians of two independent groups. It is often used when the data is ordinal or when the assumption of normality cannot be made.
Kruskal-Wallis test
The Kruskal-Wallis test is used to compare the medians of three or more independent groups. It is often used when the data is ordinal or when the assumption of normality cannot be made.
Friedman test
The Friedman test is used to compare the medians of three or more related groups. It is often used when the data is ordinal or when the assumption of normality cannot be made.
Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient
Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient is used to measure the correlation between two ordinal variables. It is often used when the assumption of normality cannot be made.
Nonparametric tests are widely used in research, particularly in fields such as psychology, sociology, and medicine. They are a valuable tool for researchers who need to analyze data that does not meet the assumptions of parametric tests.
Practice Problems: Chapter 12 Ap Stats Test
Solving practice problems is a crucial step in preparing for the Chapter 12 AP Statistics Test. These problems allow you to test your understanding of the concepts covered in the chapter and identify areas where you need further practice.
Here are a variety of practice problems that cover the different topics in Chapter 12. The answer key for these problems is provided at the end of this section.
Probability Distributions
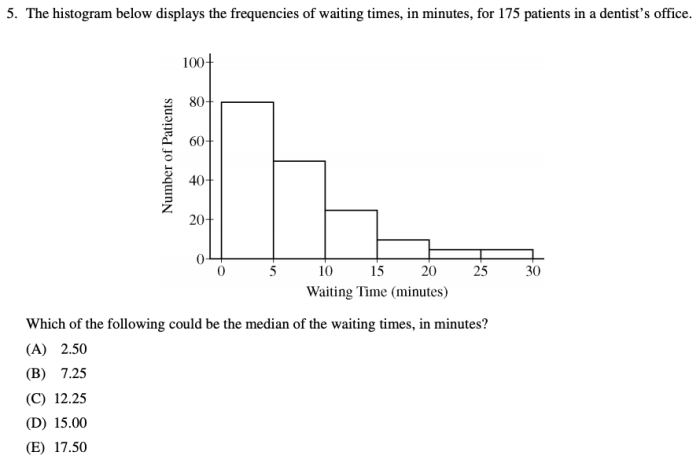
- Find the probability of rolling a 6 on a standard six-sided die.
- The time it takes for a customer to be served at a fast-food restaurant is normally distributed with a mean of 5 minutes and a standard deviation of 1 minute. What is the probability that a customer will be served in less than 4 minutes?
- A bag contains 10 red marbles, 5 blue marbles, and 3 green marbles. If two marbles are drawn from the bag without replacement, what is the probability that the first marble is red and the second marble is blue?
Sampling and Estimation
- A sample of 100 students is taken from a population of 1,000 students. The sample mean is 75. What is the 95% confidence interval for the population mean?
- A company wants to estimate the average income of its employees. They randomly select a sample of 50 employees and find that the sample mean income is $50,000. The population standard deviation is known to be $10,000. What is the 99% confidence interval for the population mean income?
Hypothesis Testing
- A company claims that their new product will increase sales by 10%. A sample of 100 customers is taken, and the sample mean increase in sales is 8%. Test the company’s claim at the 0.05 level of significance.
- A researcher wants to test if there is a difference in the mean weight of two groups of people. The first group is a control group that does not receive any treatment, and the second group is a treatment group that receives a new weight loss program.
The sample mean weight of the control group is 150 pounds, and the sample mean weight of the treatment group is 145 pounds. The sample standard deviations are 10 pounds for the control group and 8 pounds for the treatment group.
Test the researcher’s claim at the 0.01 level of significance.
Regression Analysis
- A company wants to predict the sales of their new product based on the amount of advertising they spend. They collect data on sales and advertising spending for 10 different months. The correlation coefficient between sales and advertising spending is 0.8. Interpret this result.
- A researcher wants to test if there is a linear relationship between the number of hours a student studies and their grade on a test. They collect data on the number of hours studied and the grade on the test for 20 students.
The regression line is: Grade = 50 + 2.5 – Hours. Interpret the slope of the regression line.
Correlation and Causation
- A study finds that there is a strong positive correlation between the number of hours of sleep a person gets and their overall health. Explain why this does not necessarily mean that getting more sleep causes better health.
- A study finds that there is a strong negative correlation between the amount of money a person earns and the number of crimes they commit. Explain why this does not necessarily mean that earning more money causes people to commit fewer crimes.
Nonparametric Tests
- A company wants to test if there is a difference in the median sales of two different products. They collect data on sales for 100 different customers for each product. The median sales for the first product is $100, and the median sales for the second product is $120. Test the company’s claim at the 0.05 level of significance.
- A researcher wants to test if there is a difference in the distribution of grades between two different classes. They collect data on the grades of 50 students in each class. The researcher wants to use a nonparametric test to test their claim.
Which nonparametric test should they use?
Answer Key
- 1/6
- 0.3085
- 0.105
- (71.75, 78.25)
- (46,538, 54,062)
- Fail to reject the null hypothesis
- Reject the null hypothesis
- There is a strong positive correlation between sales and advertising spending, meaning that as advertising spending increases, sales tend to increase.
- The slope of the regression line is 2.5, which means that for every additional hour a student studies, their grade on the test is expected to increase by 2.5 points.
- Correlation does not imply causation. There may be other factors that are causing both the increase in sleep and the improvement in health.
- Correlation does not imply causation. There may be other factors that are causing both the increase in income and the decrease in crime.
- Fail to reject the null hypothesis
- Mann-Whitney U test
FAQ Corner
What is the purpose of the Chapter 12 AP Statistics Test?
The Chapter 12 AP Statistics Test assesses your understanding of statistical concepts and your ability to apply them to real-world situations.
What topics are covered on the test?
The test covers a wide range of topics, including probability distributions, sampling and estimation, hypothesis testing, regression analysis, correlation and causation, and nonparametric tests.
How can I prepare for the test?
To prepare for the test, you should review the course material, practice solving problems, and take practice tests.