An investor in a t-bill earns interest by _______. – An investor in a T-bill earns interest by discounting, a unique mechanism that distinguishes T-bills from other short-term investments. This introductory paragraph delves into the intricacies of T-bill interest accrual and payment, setting the stage for a comprehensive exploration of the topic.
The subsequent paragraphs will meticulously dissect the concept of discount rate and its pivotal role in T-bill pricing. We will delve into the relationship between discount rate and market yield, examining the factors that influence their fluctuations.
Interest Accrual and Payment
Interest on T-bills accrues daily based on the face value of the bill and the annual discount rate. The interest earned is added to the bill’s purchase price and is paid at maturity.
Interest Payment at Maturity
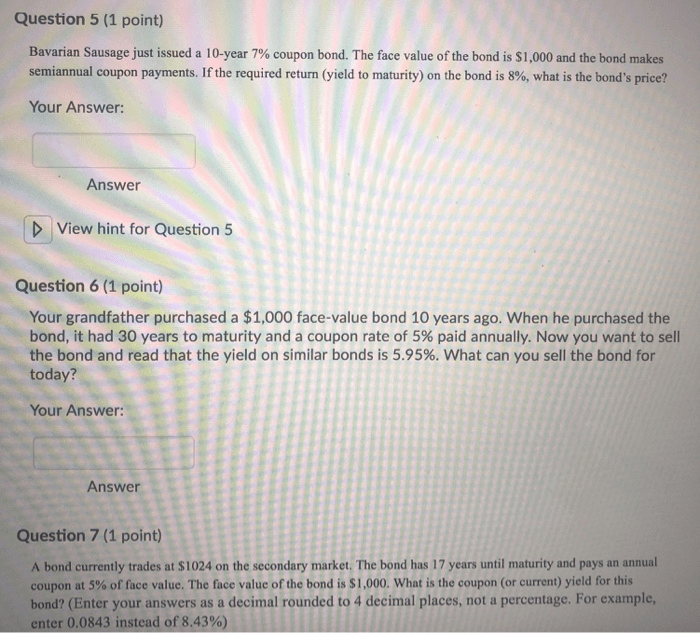
When a T-bill matures, the investor receives the face value of the bill, which includes the accrued interest. The investor’s profit is the difference between the purchase price and the face value.
For example, if an investor purchases a $10,000 T-bill with a 30-day maturity and a 2% annual discount rate, the daily interest accrual would be $10,000 x 2% / 360 = $0.56. Over the 30-day maturity period, the total interest earned would be $30 x $0.56 = $16.80.
Discount Rate and Market Yield

Discount Rate
The discount rate is the annualized interest rate used to calculate the purchase price of a T-bill. It is determined by the Treasury Department through an auction process.
Market Yield
The market yield is the annualized return an investor expects to earn on a T-bill. It is calculated by dividing the annual discount rate by 1 minus the discount factor. The discount factor is the present value of $1 received at maturity, discounted at the annual discount rate.
Relationship between Discount Rate and Market Yield
The market yield is inversely related to the discount rate. When the discount rate increases, the market yield decreases, and vice versa.
Factors Influencing Discount Rate Fluctuations
- Expectations of future interest rates
- Economic conditions
- Government borrowing needs
Risk and Return Profile
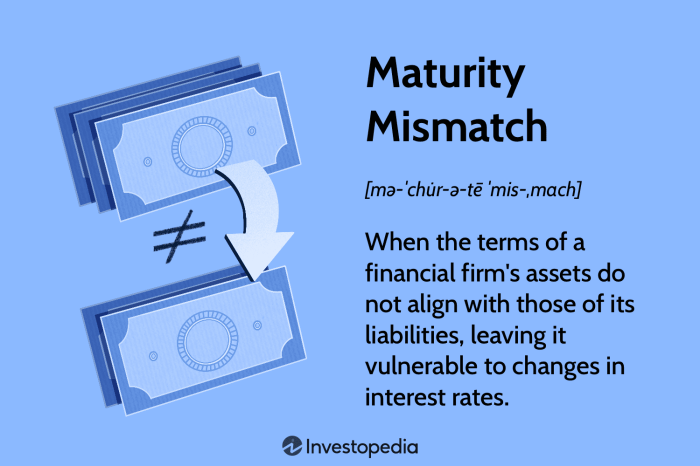
Risk-Return Profile of T-bills
T-bills are considered low-risk investments due to their short maturity and the full faith and credit of the U.S. government backing them. However, they are subject to interest rate risk, which can impact their value if interest rates change.
Comparison to Other Short-Term Investments
Compared to other short-term investments, T-bills offer a relatively low return but also carry lower risk. Money market accounts and certificates of deposit (CDs) may offer slightly higher returns but are subject to credit risk and early withdrawal penalties.
Implications of Interest Rate Changes on T-bill Returns
When interest rates rise, the value of existing T-bills falls, as investors can purchase new T-bills with higher interest rates. Conversely, when interest rates fall, the value of existing T-bills rises.
Liquidity and Market Depth
Liquidity of T-bills
T-bills are highly liquid investments, with a large secondary market where they can be bought and sold before maturity. This liquidity allows investors to easily adjust their portfolios or exit their investments.
Role of Market Makers
Market makers facilitate T-bill trading by providing bid and ask prices, ensuring a continuous market for the instruments.
T-bill Trading Volumes and Bid-Ask Spreads
T-bill trading volumes are substantial, with billions of dollars worth of T-bills traded daily. Bid-ask spreads are typically narrow, reflecting the high liquidity of the market.
Investment Strategies
Investment Strategies Involving T-bills
- Short-term cash management
- Portfolio diversification
- Interest rate hedging
Use of T-bills in Portfolio Diversification and Risk Management
T-bills can be used to diversify portfolios and reduce overall risk. By investing in T-bills with different maturities, investors can create a laddered portfolio that provides a steady stream of income and reduces interest rate risk.
T-bill-Based Investment Strategies, An investor in a t-bill earns interest by _______.
Some common T-bill-based investment strategies include:
- Cash flow matching
- Maturity laddering
- Yield curve arbitrage
FAQs: An Investor In A T-bill Earns Interest By _______.
What is the process of interest accrual on T-bills?
Interest on T-bills accrues daily based on the difference between the purchase price and the maturity value.
How is interest paid on T-bills?
Interest is paid in a lump sum at maturity when the T-bill is redeemed.
What factors influence the discount rate on T-bills?
The discount rate is influenced by factors such as inflation expectations, economic growth prospects, and the overall supply and demand for T-bills.