Section 17.4 Sound and Hearing Answer Key unlocks a fascinating journey into the realm of sound and hearing. This comprehensive guide provides a thorough understanding of the fundamental concepts, anatomy, and applications of sound, empowering readers to delve into the intricacies of this captivating field.
Delving into the properties of sound waves, we explore their frequency, amplitude, and wavelength, gaining insights into how sound is produced and transmitted. The intricate anatomy of the human ear is meticulously examined, revealing the remarkable functions of the outer, middle, and inner ear in the process of hearing.
Section 17.4 Sound and Hearing: Section 17.4 Sound And Hearing Answer Key
Section 17.4 of the textbook provides an overview of the physics of sound and the human auditory system. It covers topics such as the properties of sound waves, the anatomy of the ear, and the process of hearing. This section also discusses hearing loss, hearing protection, and the applications of sound in technology.
The key concepts covered in this section include:
- The properties of sound waves, including frequency, amplitude, and wavelength
- The production and transmission of sound waves
- The anatomy of the human ear
- The function of each part of the ear in the hearing process
- The causes and types of hearing loss
- The different ways to measure and evaluate hearing loss
- Guidelines for protecting hearing from damage
- The use of hearing protection devices, such as earplugs and earmuffs
- The applications of sound in various technologies, such as medical imaging and underwater communication
- The use of sound in music and entertainment
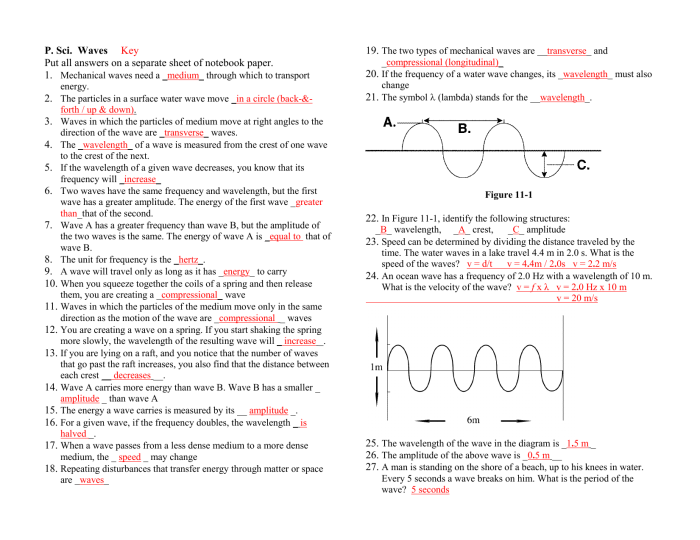
Sound Waves
Sound waves are mechanical waves that travel through a medium, such as air, water, or solids. They are produced by the vibration of an object, which causes the surrounding medium to vibrate. The properties of sound waves include:
- Frequency: The number of vibrations per second, measured in hertz (Hz)
- Amplitude: The maximum displacement of the medium from its equilibrium position
- Wavelength: The distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of the wave
Sound waves are transmitted through the medium by the transfer of energy from one particle to the next. The speed of sound in a medium depends on the density and elasticity of the medium.
The Human Ear, Section 17.4 sound and hearing answer key
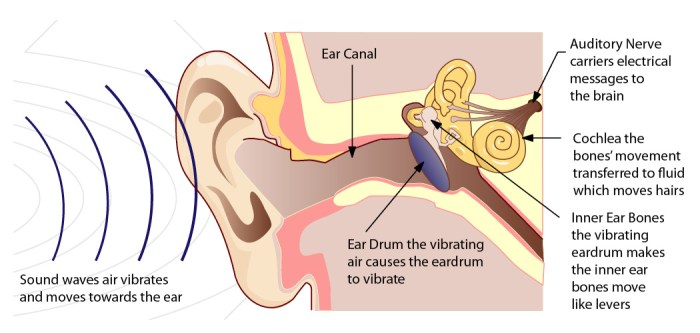
The human ear is a complex organ that is responsible for hearing. It can be divided into three main parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear.
- The outer ear consists of the pinna, which is the visible part of the ear, and the ear canal, which leads to the middle ear.
- The middle ear is a small, air-filled cavity that contains three small bones, called the ossicles. The ossicles transmit sound waves from the eardrum to the inner ear.
- The inner ear is a fluid-filled labyrinth that contains the cochlea, which is the organ of hearing. The cochlea is lined with hair cells that convert sound waves into electrical signals that are sent to the brain.
FAQ Guide
What are the key concepts covered in Section 17.4 Sound and Hearing?
Section 17.4 explores the properties of sound waves, the anatomy of the human ear, the causes and types of hearing loss, and the importance of hearing protection.
How are sound waves produced and transmitted?
Sound waves are produced by vibrations that create disturbances in the surrounding medium, such as air or water. These disturbances propagate through the medium as waves, carrying energy and information.
What are the different parts of the human ear and their functions?
The human ear consists of the outer ear, which collects sound waves; the middle ear, which amplifies sound waves and transmits them to the inner ear; and the inner ear, which contains sensory cells that convert sound waves into electrical signals.