Embark on a captivating journey with our foramina of the skull quiz! Delve into the intricate network of openings in your skull, where nerves, blood vessels, and vital structures pass through. Brace yourself for an enlightening adventure that will unravel the secrets of these enigmatic portals.
From the colossal foramen magnum to the tiny mental foramen, each opening plays a pivotal role in our anatomy and well-being. Get ready to navigate the cranial landscape, unraveling the mysteries that lie beneath the surface.
Introduction
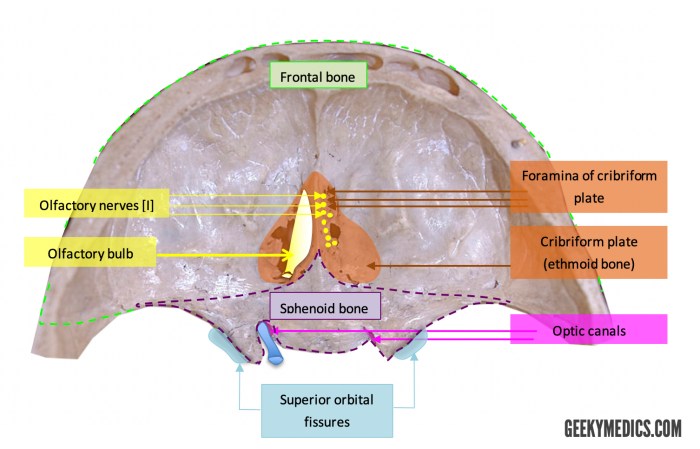
Foramina are openings in the skull that allow nerves, blood vessels, and other structures to pass through. They are essential for the proper functioning of the brain and other organs of the head and neck.
Understanding the foramina is important for medical professionals, such as neurologists, neurosurgeons, and dentists, as it helps them to diagnose and treat a variety of conditions. For example, knowing the location of the foramen magnum, which is the opening at the base of the skull through which the spinal cord passes, is important for neurosurgeons who are performing surgery on the brain or spinal cord.
Major Foramina of the Skull
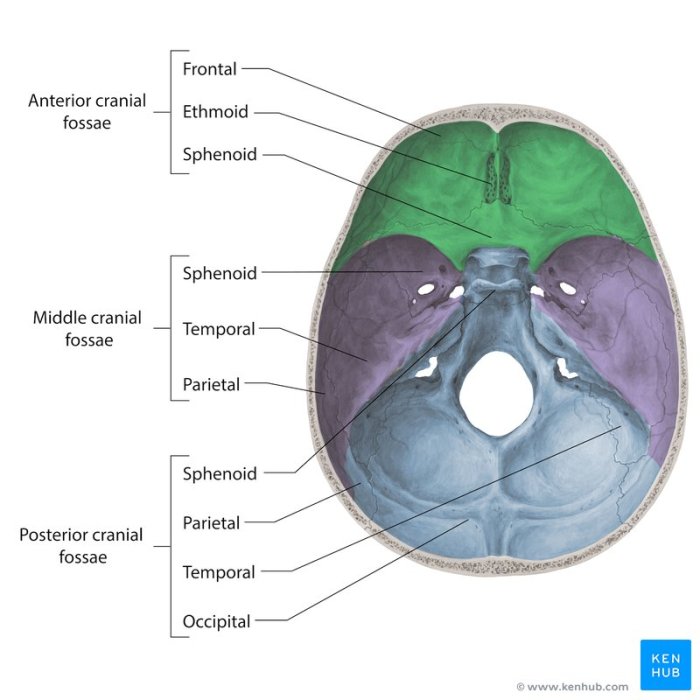
Foramen Magnum
The foramen magnum is a large, oval opening located at the base of the skull, specifically at the boundary between the occipital bone and the first cervical vertebra. It serves as a crucial passageway for the brainstem (specifically the medulla oblongata) and spinal cord to connect with each other.
Additionally, the vertebral arteries and accessory nerves pass through the foramen magnum.
Jugular Foramen
The jugular foramen is a significant opening found on the inferior surface of the temporal bone. It plays a vital role in transmitting blood and nerves between the skull and neck. The internal jugular vein, which drains blood from the brain, exits the skull through the jugular foramen.
Foramina of the skull quiz is a great way to test your knowledge of the skull’s anatomy. If you’re looking for a fun and educational way to learn more about the skull, I recommend checking out sign into my hj yearbook . The quiz is free to take and it’s a great way to challenge yourself and learn more about the skull.
Additionally, several cranial nerves, including the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX), vagus nerve (X), and accessory nerve (XI), pass through this foramen.
Optic Foramen
The optic foramen is a small, round opening situated on the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone. It is of utmost importance for vision as it allows the optic nerve (cranial nerve II) to pass from the brain to the orbit.
The optic nerve carries visual information from the retina to the brain, enabling us to perceive images.
Foramen Ovale
The foramen ovale is an opening located on the greater wing of the sphenoid bone. It serves as a passageway for the mandibular nerve, a branch of the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve V). The mandibular nerve provides sensory innervation to the lower jaw, teeth, and skin of the face.
Foramen Rotundum and Foramen Spinosum
The foramen rotundum and foramen spinosum are both located on the greater wing of the sphenoid bone. The foramen rotundum transmits the maxillary nerve, another branch of the trigeminal nerve, which provides sensory innervation to the upper jaw, teeth, and skin of the face.
The foramen spinosum allows the passage of the middle meningeal artery, which supplies blood to the dura mater, the outermost layer of the meninges that envelops the brain and spinal cord.
Minor Foramina of the Skull
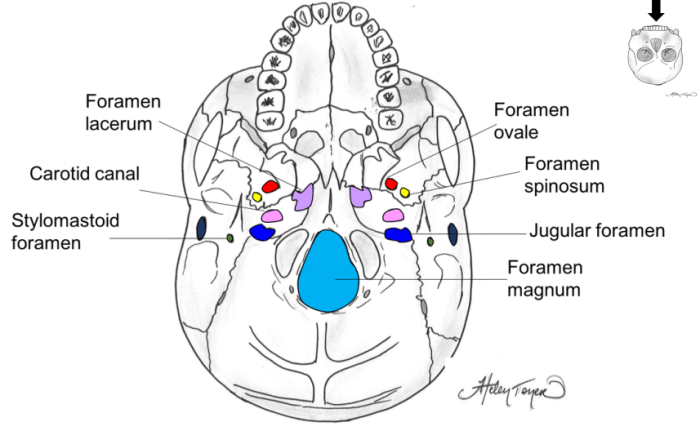
Minor foramina of the skull are smaller openings that allow nerves and blood vessels to pass through the skull. They are less significant than major foramina but still play important roles in the functioning of the head and neck.
List of Minor Foramina, Foramina of the skull quiz
| Name | Location | Function | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mental foramen | Mandible, below the second premolar tooth | Transmits the mental nerve and vessels to the lower lip and chin | May be the site of local anesthesia injections for dental procedures |
| Infraorbital foramen | Maxilla, below the orbit | Transmits the infraorbital nerve and vessels to the cheek and nose | May be the site of local anesthesia injections for dental procedures |
| Supraorbital foramen | Frontal bone, above the orbit | Transmits the supraorbital nerve and vessels to the forehead | May be the site of local anesthesia injections for headache relief |
| Foramen lacerum | Base of the skull, between the temporal bone and occipital bone | Transmits the internal carotid artery and the cranial nerves IX, X, and XI | May be involved in skull base fractures or tumors |
| Carotid canal | Temporal bone | Transmits the internal carotid artery into the cranial cavity | May be involved in skull base fractures or tumors |
Clinical Applications
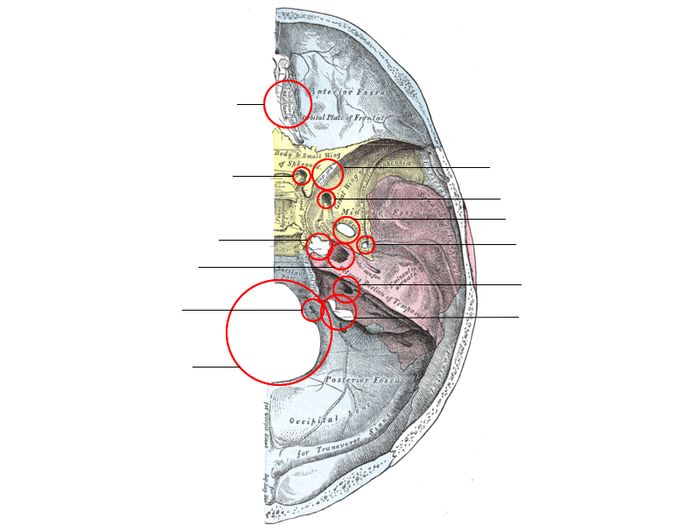
Foramina play crucial roles in surgical procedures, skull fracture diagnosis and treatment, and forensic anthropology.
In surgeries, foramina serve as landmarks for accessing specific regions of the skull or its contents. For instance, the foramen magnum provides a pathway for surgical procedures involving the brainstem or upper spinal cord.
Diagnosing and Treating Skull Fractures
Foramina can indicate the location and severity of skull fractures. Fractures near or involving foramina may damage underlying nerves or blood vessels, leading to neurological or vascular complications.
Forensic Anthropology
In forensic anthropology, foramina provide clues about an individual’s age, sex, and ancestry. The size, shape, and location of foramina can vary among different populations and can assist in identifying remains.
Detailed FAQs: Foramina Of The Skull Quiz
What is the largest foramen in the skull?
Foramen magnum
Which foramen transmits the optic nerve?
Optic foramen
What is the clinical significance of the jugular foramen?
Landmark for surgical procedures, diagnosing and treating skull fractures