Human impact in the taiga – Human Impact on the Taiga: Delving into the multifaceted effects of human activities on this vast and ecologically significant biome.
From logging and mining to recreation and climate change, human presence has left an undeniable mark on the taiga, shaping its landscapes, ecosystems, and the lives of its inhabitants.
Cultural and Social Significance of the Taiga: Human Impact In The Taiga
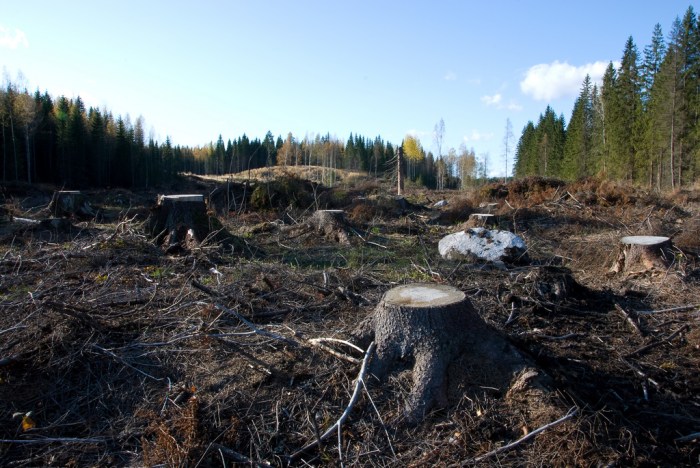

The taiga holds immense cultural and social significance for Indigenous and local communities. It provides essential resources for their livelihoods, such as food, shelter, and medicine. The taiga is also a sacred landscape, where many Indigenous and local communities have deep spiritual and cultural connections.Traditional
knowledge and practices play a vital role in the conservation and management of taiga ecosystems. Indigenous and local communities have a deep understanding of the taiga’s ecology and have developed sustainable practices that have preserved the taiga for generations. These practices include rotational hunting, selective logging, and traditional fire management techniques.
Balancing Cultural and Economic Interests, Human impact in the taiga
Balancing cultural and economic interests in the taiga is a complex challenge. The taiga is a valuable resource for both Indigenous and local communities and for the global economy. However, economic activities such as logging, mining, and oil and gas development can have negative impacts on the taiga’s ecosystems and cultural values.Finding
ways to balance these interests is essential for the long-term sustainability of the taiga. This can be achieved through collaborative management approaches that involve Indigenous and local communities in decision-making processes. It also requires the development of economic activities that are compatible with the taiga’s cultural and ecological values.
Clarifying Questions
What are the primary human activities that impact the taiga?
Logging, mining, and recreational activities are among the most significant human activities that affect the taiga.
How does climate change affect the taiga ecosystem?
Climate change leads to rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events, which can disrupt plant and animal communities and alter the overall structure and function of taiga ecosystems.
What are some strategies for conserving the taiga?
Protected areas, sustainable forestry practices, and community-based conservation initiatives play a vital role in mitigating human impacts and maintaining the integrity of taiga ecosystems.
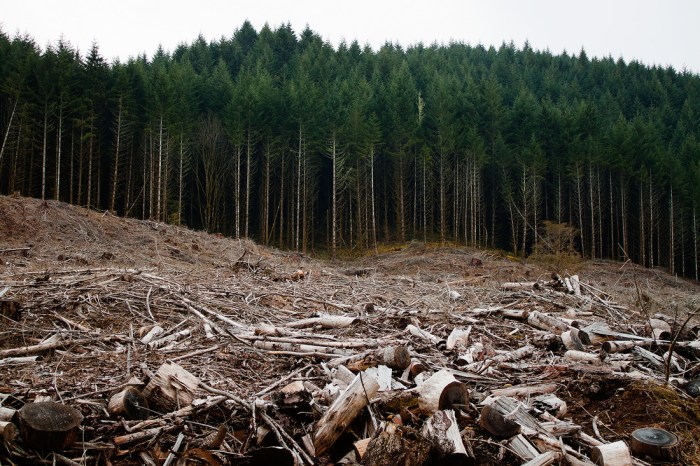


The taiga, the world’s largest terrestrial biome, is facing significant human impacts, including deforestation and climate change. To understand the extent of these impacts, accurate data is crucial. When measuring the area of deforested land, it’s important to consider the number of significant figures in the measurement.
For instance, if the area is reported as 8000 hectares, we need to know how many significant figures it has (hint: how many sig figs in 8000 ). This information helps us determine the precision of the measurement and make informed decisions about conservation efforts in the taiga.